Prerequisites for Operator nodes
CXT Stake
Before you get started, make sure you have: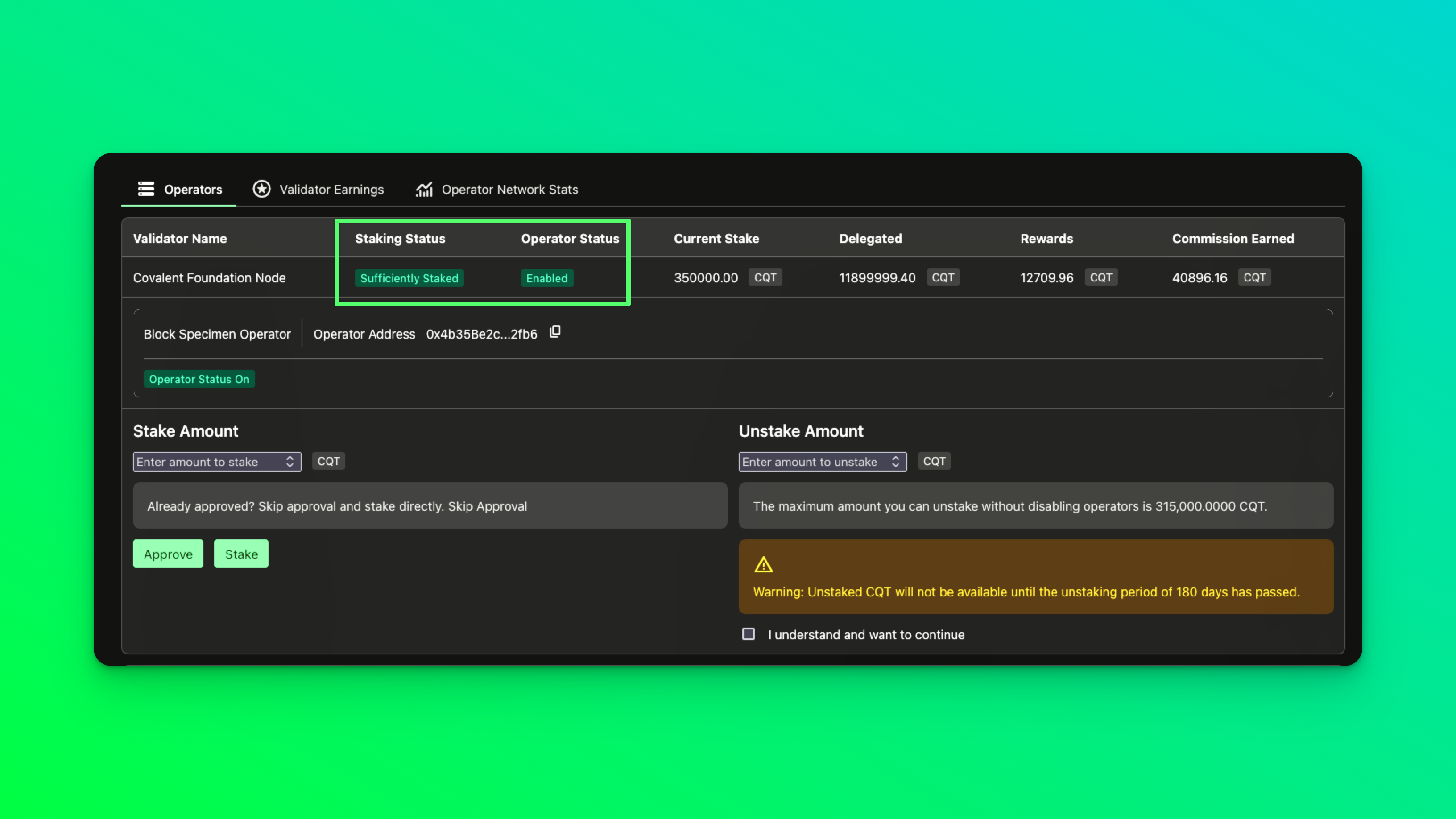
- the minimum self-stake CXT available, currently 175K CXT
- your operator address is added and enabled on the operator dashboard

Install Dependencies
MacOS 12.x (M1/Intel) Installation requirements
Install XCode
- You must also Install brew (for mac m1/intel)
Git, Golang, Redis.
Gitis used as the source code version control manager across all our repositories.Gois the programming language that is used to develop ongo-ethereumand bsp patches, the agent given below is also entirely written in Go.Redisis our in-memory database, cache and streaming service provider.
Go Version: Go 1.22 or later
MacOS 12.x (M1/Intel)
Debian/Ubuntu
Fedora
RHEL/CentOS
Install Git, Golang, RedisOpenSUSE/SLES
Install Git, Golang, RedisLet’s now start with Environment Setup before running Node, Here, you need to setup the following;
- BSP-Geth & Lighthouse
- DAS-Pinner Setup
- BSP-Agent Setup
1. BSP-Geth & Lighthouse Setup :
Clone Repo
Note: The current BSP-Geth version is v2.2.0-bsp. For the latest updates or additional details, please check the announcements or discussions in Discord.
Build geth
Build geth (install go if you don’t have it) and other geth developer tools from the root repo with (if you need all the geth related development tools run make all )
Start redis (our streaming service) with the following
Build geth (install go if you don’t have it) and other geth developer tools from the root repo with (if you need all the geth related development tools run make all )
Start redis-cli
Start
We are now ready to start accepting stream message into redis local
redis-cli in a separate terminal so you can see the encoded bsps as they are fed into redis streams. We are now ready to start accepting stream message into redis local
- Go back to
~/bsp-gethand start geth with the given configuration, here we specify the replication targets (block specimen targets) with Redis stream topic key replication, in snap syncmode. - Prior to executing, please replace
$PATH_TO_GETH_MAINNET_CHAINDATAwith the location of the mainnet snapshot that you will be downloading in the next step via lighthouse. Everything else remains the same as given below. - Please review the flags and use them according to your system need
Each of the bsp flags and their functions is described below
--mainnet- lets geth know which network to synchronize with, this can be--ropsten,--goerlietc
--discv5=true- Enables the node to participate in the Ethereum network’s Discovery v5 protocol, which is used for finding peers.
--txlookuplimit- Disables the limitation on how far back in the chain transactions are indexed, allowing for retrieval of transaction data from any block in the node’s history.
--cache- Sets the memory allocation for the node’s cache in megabytes, which is used to improve performance by holding recently accessed data.
--syncmode- this flag is used to enable different syncing strategies for geth and a full sync allows us to execute every block from block 0; while snap allows us to execute from live blocks
--light.ingress- Limits the bandwidth in kilobytes per second that the node dedicates to serving light clients on Ingress (incoming traffic).
--light.egress- Limits the bandwidth in kilobytes per second that the node dedicates to serving light clients on Egress (outgoing traffic).
--light.maxpeers- Sets the maximum number of light client peers that the node can connect to.
--http- Enable the HTTP-RPC server
--http.addr- HTTP-RPC server listening interface (default: localhost)
--http.api- API’s offered over the HTTP-RPC interface(default: eth,net,web3)
--http.vhosts- Allows all virtual hostnames to access the HTTP-RPC server, effectively disabling the host-based security check.
--ws- Enable the WS-RPC server
--ws.addr- WS-RPC server listening interface (default: localhost)
--ws.api- API’s offered over the WS-RPC interface (default: eth,net,web3)
--ws.origins- Origins from which to accept WebSocket requests
--datadir- specifies a local datadir path for geth (note we use “bsp” as the directory name with the Ethereum directory), this way we don’t overwrite or touch other previously synced geth libraries across other chains
--authrpc.jwtsecret- Specifies the path to the JWT secret file used for authentication in the RPC API, providing an additional layer of security by requiring tokens for access.
--replication.targets- this flag points to redis, and lets the bsp know where and how to send the bsp messages (this flag will not function without the usage of either one or both of the flags below if both are selected a full block-replica is exported)
--replica.result- this flag lets the bsp know if all fields related to the block-result specification need to be exported (if only this flag is selected the exported object is a block-result)
--replica.specimen- this flag lets the bsp know if all fields related to the block-specimen specification need to be exported (if only this flag is selected the exported object is a block-specimen)
—replica.blob- Enables the extraction of blob specimens as part of the complete block specimen export, which includes state specimens and transaction receipts, collectively referred to as a block replica. This flag is used to include additional block content, particularly useful for nodes participating in more extensive data analysis or archiving, ensuring comprehensive block data is available for these purposes.
--log.file- specifies the file location where the log files have to be placed. In case of error (like permission errors), the logs are not recorded in files.
Install Lighthouse
bsp-geth also needs a consensus client. We’ve tested and found the lighthouse to be stable and works well. Goto the installation instructions to install it.
There are multiple versions of lighhouse available Recommended is to use Pre-built binaries -> releases on github -> Then find a version where the Breaking Changes are none (i.e currently Summer Smith Prime v7.0.1) or you can ask us on the discord for assistance with the version.
Then run the lighthouse using:
Sample Service systemmd file for lighthouse can be found here.
Note: The current lighthouse stable version is v7.0.1. For the latest updates or additional details, please check the announcements or discussions in Discord.
Wait for the
eth blockchain to sync to the tip. Connect to the node’s ipc instance to check how far the node is syncedOnce connected, wait for the node to reach the highest known block to start creating live block specimens
The last two logs show that new block replicas containing the block specimens are being produced and streamed to the redis topic
replication. After this you can check that redis is stacking up the bsp messages through the redis-cli with the command below (this should give you the number of messages from the stream)
go-ethereum and running the bootnode helper.
NOTE: To use the bootnode binary execute make all in place of make geth, this creates all the additional helper binaries that bsp-geth ships with.
2. DAS-Pinner Setup
DAS-Pinner serves as the interface to the storage layer of the network. It’s a lightweight IPFS service that stores and pins data on the IPFS network using web3.storage. It is designed to work seamlessly with the DAS Light-Client, enabling the retrieval of data from the IPFS network and its verification using the DAS protocol.It is meant for uploading/fetching network artifacts (like block specimens and block results or any other processed block data) files of the Covalent Decentralized Network. Current :
Go Version: go1.22 or later , this could change later in time please cross check with operator-releases channel on discord for correct versions.
Note: The current DAS-Pinner stable version is v0.17.6. For the latest updates or additional details, please check the announcements or discussions in Discord.
Clone & Build
Clone and build das-pinner (in a separate folder) We store the block specimens in the ipfs network. Bsp-agent interacts with the das-pinner server to handle the storage/retrieval needs of the network.
Setting up w3cliAdditionally, you can manually install any missing dependencies.
Software Prerequisite - Node.Js version 18 or higher and npm version 7- Install w3cli Version 7.9.1: To install version 7.9.1 of the w3cli tool globally on your system, run the following command:
- Troubleshooting: If you encounter any issues, such as missing dependencies, try clearing the npm cache and reinstalling w3cli:
Get the agent key, did and delegation proof from Covalent, then you can run the ipfs-pinner
ipfs-pinner can be run as a server and allows two functionalities currently -
/get and /upload
With this, the ipfs-pinner is setup and can upload/fetch network artifacts.Sample Service systemmd file for ipfs-pinner can be found here.3. BSP-Agent Setup:
Install Dependencies
- Install direnv
MacOS 12.x (M1/Intel)
Debian/Ubuntu
Fedora
RHEL/CentOS
SLES/OpenSUSE
direnv manages and controls sensitive information for the agent, such as Ethereum private keys for operator accounts on the Covalent Network and Redis access passwords. This is crucial since these applications, exposed on HTTP ports, must not log sensitive data.To enable direnv on your machine add these to your
~./bash_profile or ~./zshrc depending on which you use as your default shell after installing it using brew. For bash users - add the following line to your
~/.bashrc For zsh users - add the following line to your
~/.zshrc